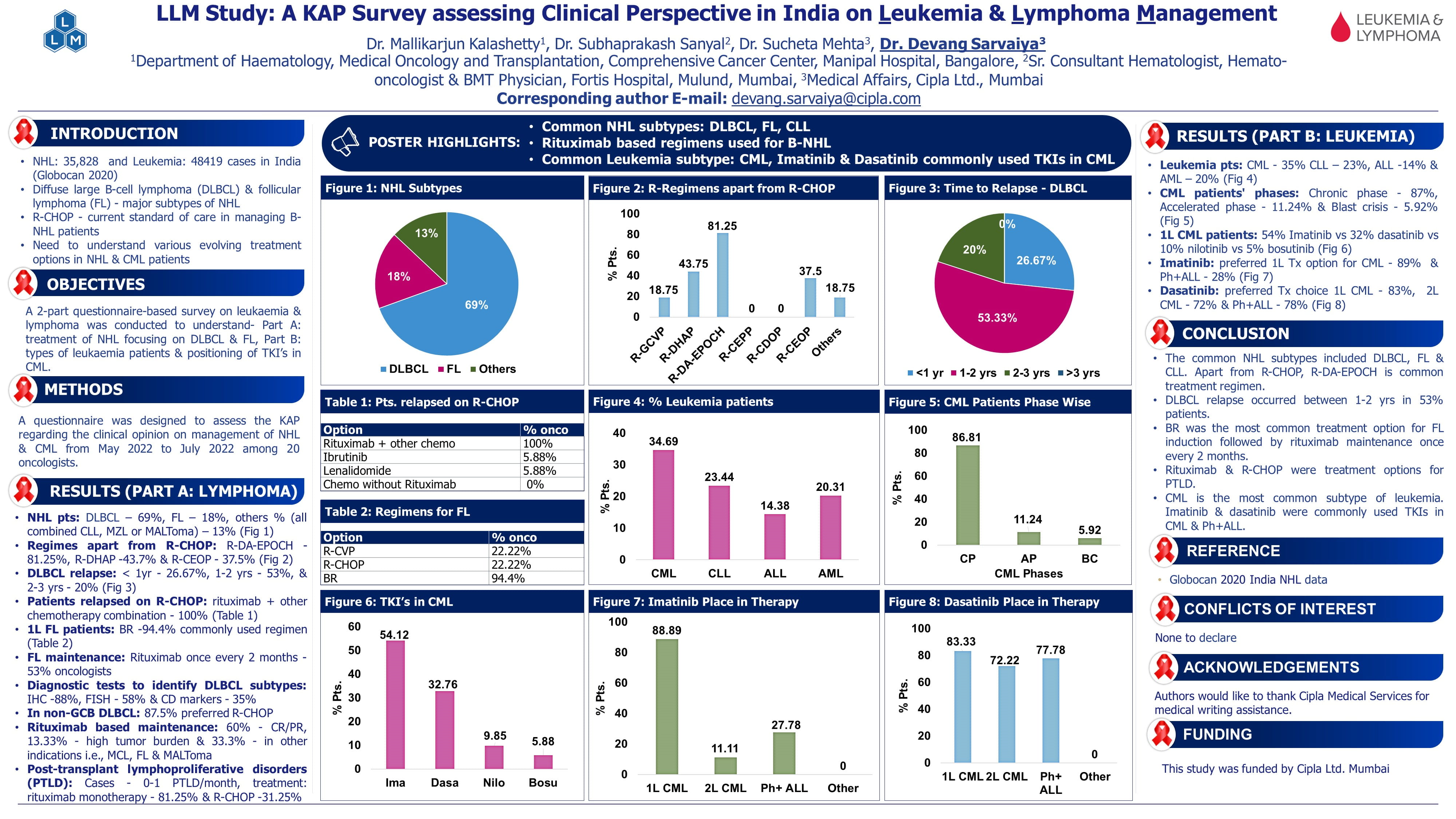
ASH 2025: Highlights from Day 1
Primary Results from EQUATOR, a Phase 3 Double-Blind, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating Itolizumab in Combination with Corticosteroids as Initial Treatment of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease.
Presenter: John Koreth
- The EQUATOR Phase 3 trial evaluated itolizumab plus corticosteroids as first-line therapy in patients with high-risk acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD; defined as Grade III-IV or Grade II with lower gastrointestinal involvement).
- A total of 158 adults (median age 59) were randomized after 72 hours of initiating corticosteroid (CS) treatment, to receive either itolizumab [1.6 mg/kg x1 followed by 0.8 mg/kg x6 doses q2 weeks (w)] or placebo (7 doses q2w).The complete response (CR) rates on day 29 were 43.0% for itolizumab vs. 48.1% for placebo (p=0.774). ORR at Day 29 was 62.0% vs 54.4% for itolizumab vs placebo (p=0.404, NS).
- Meaningful increase in the key secondary endpoint DCR was observed for itolizumab vs placebo (29.7% vs 16.2%, p=0.058, NS).
- Durable CR (Day 29–99) was higher with itolizumab (29.7% vs. 16.2%, p=0.058), and median CR duration was significantly longer (336 vs. 72 days; HR 0.38, p=0.017).
- Failure-free survival improved in the patients treated with itolizumab (HR 0.66, p=0.043). One-year OS was 66.7% vs. 49.6%, and mortality (NRM) was 28.9% vs. 41.7%.
- No new safety concerns emerged.
- The findings underscore the favorable risk profile of itolizumab and indicate that this enhanced response durability may provide meaningful clinical benefit for treated patients.
Reference
Koreth J et al, Primary Results from Equator, a Phase 3 Double-Blind, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating Itolizumab in Combination with Corticosteroids as Initial Treatment of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-11633.
Dexamethasone, Rituximab and Cyclophosphamide with Bortezomib is a Rapidly Acting and Highly Efficient First-Line Treatment in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: Final Analysis of ECWM-1 Trial of the European Consortium for Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (ECWM)
Presenter: Morel P
- In the ECWM-1 trial, 202 treatment-naive patients (median age; 68 yrs) with Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (WM) were randomized to receive either dexamethasone, rituximab and cyclophosphamide (DRC, n=100) or bortezomib plus DRC (B-DRC, n=102) over six 4-week cycles.
- As per the initial findings from the trial, at a median follow-up period of 27.5 months, B-DRC induced deep and fast remission with no significant difference in the 2-year PFS, as compared to DRC alone. After 68.8 months of follow-up, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 56.7 months for B-DRC vs. 50.1 months for DRC (p=0.64), with a 2-year PFS of 79% (95% CI: 73–85). CR/VGPR rates were 35.4% for B-DRC vs. 22.2% for DRC (p=0.32).
- The median 5-year overall survival was 90% (89% for B-DRC and 91% for DRC).
- Grade ≥3 toxicities were mainly hematologic; peripheral neuropathy was 2.5-times more frequent with B-DRC. Mutational status (MYD88 and CXCR4) did not affect outcomes.
- These findings support fixed-duration immunochemotherapy with DRC as a standard first-line WM treatment, with B-DRC offering faster, deeper responses but no significant long-term advantage. The ongoing VIWA-1 trial will compare DRC to venetoclax-rituximab.
Reference
Morel P et al, Dexamethasone, Rituximab and Cyclophosphamide with Bortezomib is a rapidly acting and highly efficient first-line treatment in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: Final analysis of ECWM-1 trial of the European Consortium for Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (ECWM). 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-12054.
Venetoclax Combined with Five Days of Azacitidine for the Treatment of Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Initial Results of the Prospective Venaza-5S Trial
Presenter: Klaus Metzeler
- The Phase II Ven-Aza-5S trial ascertained the safety and tolerability of 5-day treatment with azacitidine (AZA) combined with 28d of venetoclax (VEN) in 45 newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients who were ineligible for standard induction therapy (median age 81 years).
- Patients received AZA 75 mg/m² on days 1–5 and VEN 400 mg on days 1–28 per 28-day cycle.
- The composite complete remission (cCR; defined as the rate of CR or CR with incomplete hematopoietic recovery after up to 6 cycles of therapy) rate was 53.3%, and overall response rate (ORR) was 60%.
- Median follow-up period was 11.5 months, and median overall survival was 11.1 months.
- Grade ≥3 hematologic toxicities occurred in 67%, and infections in 38%. Day 30 mortality was 11%.
- Compared to the VIALE-A trial (cCR 66% with 7-day AZA), this 5-day Ven-AZA regimen showed promising efficacy and tolerability, supporting its potential as a frontline option for older or comorbid AML patients.
Reference
Metzeler K et al, Venetoclax combined with five days of azacitidine for the treatment of previously untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Initial results of the prospective venaza-5S trial. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-2432.
Ibrutinib plus R-CHOP Followed by Maintenance in Untreated ABC-DLBCL Patients with IPI ≥2: A First Analysis of Phase II Study FIL_RI-CHOP
Presenter: Alice Di Rocco.
- Patients with ABC subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) have poor outcomes with R-CHOP. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKi) show better responses in non-GCB DLBCL.
- The FIL_RI-CHOP phase II trial evaluated R-CHOP + ibrutinib followed by maintenance in untreated, high-risk ABC-DLBCL patients aged <65.
- Of 279 registered, 75 ABC cases received experimental therapy. Interim ORR was 90.7%, with 21.3% complete responses; end-of-induction PET-CT showed 85.3% ORR and 72% metabolic CR.
- Safety was manageable, with neutropenia and mild gastrointestinal/neurological AEs most common.
- Findings suggest R-CHOP plus ibrutinib appears feasible and effective, achieving >70% metabolic CR with a manageable safety profile in young, high-risk ABC-DLBCL patients. R-CHOP plus ibrutinib may represent a safe, effective, and potentially cost-effective treatment strategy in this population.
Reference
Rocco AD et al, Ibrutinib plus R-CHOP followed by maintenance in untreated ABC-DLBCL patients with IPI ≥2: A first analysis of phase II Study FIL_RI-CHOP. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-11784.
Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone (KRd) Versus Bortezomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (VRd) in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (NDMM) – Interim Results from The Randomized Phase III COBRA Trial.
Presenter: Dominik Dytfeld
- The phase III COBRA trial (n=250) compared KRd (carfilzomib, lenalidomide, dexamethasone) versus VRd (bortezomib, lenalidomide, dexamethasone) in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM).
- After 35 months’ median follow-up, KRd showed superior efficacy: MRD-negative complete response at 12 months was higher (31% vs 18%; p=0.016), and progression-free survival favored KRd (median not reached vs 49 months; HR=0.57; p=0.0095).
- Overall response rates were similar (94% vs 91%), but KRd achieved more CR or better (71% vs 53%).
- Grade ≥3 adverse events occurred in 72% (KRd) vs 62% (VRd), with more neutropenia and cardiac events in KRd. Peripheral neuropathy was markedly lower with KRd.
- The randomized phase III COBRA trial showed superior efficacy of KRd compared VRd in NDMM supporting further evaluation of KRd-based induction regimens.
Reference
Dytfeld D et al, Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (VRd) in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) – interim results from the randomized Phase III COBRA trial. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-10191.
Efficacy and Safety Results from The Primary Analysis of The Pivotal SUMMIT Trial: Bezuclastinib in Adults with Non-Advanced Systemic Mastocytosis
Presenter: Lindsay Rein
- Systemic mastocytosis (SM) involves mast cell infiltration and mediator release; Non-advanced SM (ISM 82%, BMM 11%, SSM 7%) is most common. KIT D816V mutation occurs in ~95% of cases.
- In the Phase 2 SUMMIT trial (179 patients; median age 51; 65.9% female), bezuclastinib 100 mg QD significantly improved symptoms at 24 weeks: MS2D2 TSS change –24.3 vs –15.4 (placebo-adjusted –8.9; P=0.0002). ≥50% serum tryptase reduction: 87.4% vs 0% (P<0.0001).
- KIT VAF, BM mast cells, and ≥30% TSS reduction also improved (P≤0.01).
- Most TEAEs were grade 1; common events included hair color change (69.5%) and nausea (22%). ALT/AST ≥Gr3: 5.9%, all resolved.
- Results support bezuclastinib 100 mg QD as an effective,reduced SM burden & symptoms, well-tolerated therapy for NonAdvSM and a potentially disease-modifying impact.
Reference
Rein L et al, Efficacy and safety results from the primary analysis of the pivotal summit trial: Bezuclastinib in adults with non-advanced systemic mastocytosis. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-1593.
Impact of Lenalidomide Pre-apheresis on Markers of T Cell fitness and Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Patients with Suboptimal Response to Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation
Presenter: Hao Tang
- The KarMMa-2 phase 2 trial evaluated idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), a BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy, in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients with poor response to ASCT. While ide-cel showed strong efficacy, some patients responded inadequately, emphasizing the need to improve T-cell fitness post ASCT. This study compared Cohort 2c (BOR < VGPR) and Cohort 3 (< CR) to assess lenalidomide pre-apheresis impact.
- ORR was 87.1% and CRR 80.6% in C2c, while C3 showed superior pharmacodynamic activity, including 93.3% sBCMA clearance versus 77.4% in C2c. Immune profiling revealed improved T-cell health in C3, with lower exhaustion markers (PD1, CD38) and higher IL2, IL7, and perforin levels. Drug product analysis indicated enhanced potency and cytolytic potential in C3.
- A cycle of LEN pre-apheresis improved T-cell fitness and enhanced PD activity, resulting in better CAR T-cell phenotype and clinical response, supporting its integration into ASCT-CAR T sequencing strategies.
Reference
Tang H et al, Impact of Lenalidomide Pre-apheresis on Markers of T Cell fitness and Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Patients with Suboptimal Response to Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-9163.
Long-term Follow-up of Azacitidine, Venetoclax, and Gilteritinib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed FLT3-mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Presenter: Roberta S. Azevedo
- Patients with newly diagnosed (ND) FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) ineligible for intensive chemotherapy have poor outcomes with azacitidine and venetoclax (VEN).
- This phase II trial evaluated azacitidine, VEN, and gilteritinib (GILT) in this population. Thirty patients (median age 71 years; 73% FLT3-ITD, 27% FLT3-TKD) received the triplet regimen.
- At >3-year follow-up (median 41.5 months), complete remission/CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CR/CRi) was 96%, and measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity was 93%.
- Median relapse-free survival (RFS) was 23.4 months (3-year RFS: 43%), and median overall survival (OS) was 29.7 months (3-year OS: 46%).
- Outcomes were superior for FLT3-TKD (3-year OS: 75%) versus FLT3-ITD (36%).
- No unexpected adverse events occurred; most common grade ≥3 events were infection (63%) and febrile neutropenia (40%).
- Azacitidine, VEN, and GILT achieved durable remissions and encouraging survival, supporting randomized trials versus standard therapy.
Reference
Azevedo R et al, Long-term Follow-up of Azacitidine, Venetoclax, and Gilteritinib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed FLT3-mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-14054.
Efficacy and Safety of Benralizumab in Patients with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: Results from the Phase 3 NATRON Study
Presenter: Princess Ogbogu
- NATRON (NCT04191304) is a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating benralizumab, an anti–IL-5 receptor α antibody, in patients (pts) ≥12 years with hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES; AEC ≥1×10⁹/L, FIP1L1::PDGFRA-negative).
- Among 133 pts (median age 51 years), benralizumab significantly reduced risk of first HES flare vs placebo (HR: 0.35; P=0.0024), lowered annualized flare rate (0.41 vs 1.23; RR: 0.34; P=0.0008), and delayed hematologic relapse (HR: 0.08; P<0.0001).
- Sustained AEC <0.5×10⁹/L occurred in 91% vs 12% (OR: 87.87; P<0.0001). Fatigue improved by Week 4 (LS mean difference: –4.72; P=0.0017).
- AE were experienced by 43 (64.2%) and 44 (66.7%) pts in the benralizumab and PBO arms respectively.
- Benralizumab added to standard therapy significantly improved flare control, hematologic relapses, and fatigue, with a safety profile consistent with prior studies demonstrating clinical and biological efficacy of benralizumab in pts with HES.
Reference
Ogbogu P et al, Efficacy and Safety of Benralizumab in Patients with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: Results from the Phase 3 NATRON Study. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-3954.
Marstacimab Prophylaxis in Participants with Hemophilia A or B with Inhibitors: Results from The Phase 3 BASIS Trial
Presenter: Davide Matino
- Marstacimab, a monoclonal antibody inhibiting tissue factor pathway inhibitor, was evaluated in the phase 3 BASIS trial for males ≥12 to <75 years (N=60) with severe hemophilia A (FVIII <1%) or moderately severe to severe hemophilia B (FIX ≤2%) and current or historical high-titer inhibitors (≥5 BU/mL).
- After a 6-month observational phase (OP) on bypassing agents (on-demand [OD] or routine prophylaxis [RP]), participants received a 300 mg loading dose followed by 150 mg weekly subcutaneous marstacimab for 12 months.
- Of 60 enrolled, 51 transitioned to active treatment (ATP). Mean annualized bleeding rate (ABR) for treated bleeds decreased from 19.78 (95% CI: 16.12–24.27) in OP to 1.39 (95% CI: 0.85–2.29) in ATP (ABR ratio 0.07; P<0.0001), with consistent superiority across bleed types.
- Marstacimab was also superior vs OD therapy in all patient-reported HRQoL endpoints, except EQ-visual analog scale (VAS).
- Adverse events occurred in 74.5%, mostly mild/moderate; one serious treatment-related rash led to discontinuation. No deaths or thrombotic events were reported.
- In pts with Hemophila A or Hemophilia B and inhibitors, subcutaneous marstacimab QW significantly reduced ABR for all bleeding related endpoints vs prior OD therapy and improved HRQoL.
Reference
Matino D et al, Marstacimab Prophylaxis in Participants with Hemophilia A or B with Inhibitors: Results from The Phase 3 BASIS Trial. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-9156.
Rusfertide or Placebo Plus Current Standard-Of-Care Therapy for Polycythemia Vera: Durability of Response and Safety Results Through Week 52 from the Randomized Controlled Phase 3 VERIFY Study
Presenter: Andrew Kuykendall
- Rusfertide, a first-in-class hepcidin mimetic self-administered weekly via subcutaneous injection, was evaluated in the phase 3 VERIFY trial for patients with polycythemia vera requiring frequent phlebotomies (PHLs).
- In Part 1a (Weeks 0–32), rusfertide plus standard-of-care significantly reduced PHLs and improved hematocrit (Hct) control.
- Part 1b (Weeks 32–52) assessed durability of response and efficacy in patients crossing over from placebo (PBO).
- Of 293 randomized patients (rusfertide: n=147; PBO: n=146), 274 entered Part 1b; median rusfertide exposure was 61 weeks. Among patients initially on rusfertide, 61.9% maintained absence of PHL eligibility through Week 52.
- After crossing over from PBO, absence of PHL eligibility increased from 32.9% at Week 32 to 78.0% by Week 52.
- Median time to first PHL remained not reached and mean Hct stayed <43% throughout Part 1b in rusfertide-treated patients. Median time to first Hct ≥45% was 21.1 weeks in crossover patients.
- Patient-reported outcomes (PROMIS Fatigue SF8a, MFSAF TSS7) showed durable improvements in rusfertide group.
- Common adverse events included injection site reactions (47.4%), anemia (25.6%), and fatigue (19.6%), mostly grade 1–2; serious AEs occurred in 8.1%. Rusfertide met primary and key secondary endpoints and provided durable, sustained control of Hct <45% and a relative absence of PHL up to Week 52 with consistent safety profile across all subgroups. Similar results were observed after cross over from PBO to rusfertide.
- Rusfertide met the primary and all 4 key secondary endpoints in VERIFY and continued to provide durable, sustained control of Hct <45% and a relative absence of PHL up to Wk 52. This benefit was maintained across all subgroups, including age, PV risk category, and ongoing CRT.
Reference
Kuykendall A et al, Rusfertide or Placebo Plus Current Standard-Of-Care Therapy for Polycythemia Vera: Durability of Response and Safety Results Through Week 52 from the Randomized Controlled Phase 3 VERIFY Study. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-4119.
Phase II Frontline Chemolight R-Pola-Glo Trial Induces High and Durable Response Rates in Elderly and Medically Unfit/Frail Patients With Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma
Presenter: Björn Chapuy
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) predominantly affects older adults, and standard anthracycline-based regimens (R-CHOP/Pola-R-CHP) are often unsuitable for frail or medically unfit patients.
- The phase II AGMT-NHL-16/GLA2022-10/IKF062 trial evaluated R-Pola-Glo, a chemotherapy-free regimen combining rituximab (R), polatuzumab vedotin (Pola), and glofitamab (Glo), in N=80 previously untreated elderly/frail or unfit patients (median age 80; 19% >85 years).
- Most had advanced-stage disease (64%) and high-risk IPI (IPI 3-4, 64%). Treatment included 12 cycles (q3w). Cycle 1 included obinutuzumab, Pola, and step‑up Glo (2.5/10 mg); cycles 2‑6 combined R, Pola, and Glo at 30 mg; cycles 7‑12 consisted of Glo consolidation (30 mg). Therapy adherence was high (80% completed all cycles).
- Overall response rates were 96%, 94%, and 90% at cycles 2, 6, and end of treatment, respectively; complete metabolic response (CMR) rates were 58%, 75%, and 81%, with frequent late conversions during consolidation.
- At 15-month median follow-up, 1-year PFS, EFS, and OS were 85%, 82%, and 90%, respectively.
- Toxicities were manageable: grade 3–5 infections occurred in 22% (including 3 fatal), cytokine release syndrome in 31% (mostly low grade), and ICANS in 4%. No unexpected safety signals emerged.
- R-Pola-Glo achieved high and durable CMR rates with favourable survival outcomes, expected and manageable safety profile, supporting its further evaluation as a frontline option for frail/unfit DLBCL patients.
Reference
Chapuy B et al, Phase II Frontline Chemolight R-Pola-Glo Trial Induces High and Durable Response Rates in Elderly and Medically Unfit/Frail Patients With Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-12999.
Comparison of Axi-Cel versus Liso-Cel as 2nd Line Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Real-Life: A Lysa Study from the Descar-T Registry
Presenter: Gabriel Brisou
- In DESCAR-T registry analysis, large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) patients were treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) (n=663) or lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) (n=142) as second-line anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. The median follow-up was 12.9 months for axi-cel and 7.7 months for liso-cel.
- Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) showed no significant differences between axi-cel and liso-cel.
- Complete response rates were similar (62.6% vs 65.8%), while overall response rate favored liso-cel (90% vs 79.8%, P=0.008).
- Toxicity was higher with axi-cel (all P<0.001): more frequent cytokine release syndrome (93.9% vs 50.8%), severe neurotoxicity (17.6% vs 0.2%), and ICU transfers (22.4% vs 5.3%).
- After PS-weighting in a large French population with CAR T-cell therapy for 2L LBCL, there was no significant OS or PFS difference between axi-cel and liso-cel. However, axi-cel had a greater incidence of severe neurotoxicity. These results require confirmation in a larger liso-cel cohort with longer follow-up.
Reference
Brisou G et al, Comparison of Axi-Cel versus Liso-Cel as 2nd Line Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Real-Life: A Lysa Study from the Descar-T Registry. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-12398.
Results of the Primary End-Point of the LOC-R01: A Randomized Phase II Study of Lenalidomide and Ibrutinib in Association with Rituximab-Methotrexate Procarbazine Vincristin (R-MPV) as a Targeted Induction Treatment for Patients Aged 18 to 65 with a Newly Diagnosed Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL)
Presenter: Carole Soussain
- The LOC-R01 phase II trial assessed the effectiveness of R-MPV first-line induction therapy plus either lenalidomide (15 mg/day, D1-D21) or ibrutinib 560 mg daily as a targeted induction therapy for four induction cycles in 92 immunocompetent newly diagnosed PCNSL patients.
- The complete response (CR)/CR unconfirmed (CR/CRu) rates were 86% with lenalidomide and 82% with ibrutinib, exceeding the efficacy threshold (≥65%). More patients on ibrutinib (87%) proceeded to autologous stem cell transplantation (75% with lenalidomide).
- At 18 months, progression-free survival was 72% vs. 82% and overall survival was 87% vs. 88% for lenalidomide and ibrutinib arms, respectively.
- Toxicities were manageable and consistent. A decrease in the CD4+ and an increase in the activation markers PD-1 and ICOS were seen with ibrutinib, whereas Treg cells rose with lenalidomide.
- Both arms met the predetermined threshold of efficacy with 86% and 82% of CR/CRu rates in the lenalidomide and ibrutinib arm, respectively.
- Both regimens, R-MPV plus a BTK-inhibitor or an immunomodulatory drug constituted an interesting first-line induction for PCNSL patients up to 65y. Biomarker and immune profiling analyses are ongoing to guide therapy selection.
Reference
Soussain C et al, Results of the Primary End-Point of the LOC-R01: A Randomized Phase II Study of Lenalidomide and Ibrutinib in Association with Rituximab-Methotrexate Procarbazine Vincristin (R-MPV) as a Targeted Induction Treatment for Patients Aged 18 to 65 with a Newly Diagnosed Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL). 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-12054.
Zanubrutinib, Rituximab, and High-dose Methotrexate as First-line Treatment in Newly Diagnosed Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (Zana): A Prospective, Single-arm Study
Presenter: Zhizhou Xia
- This prospective, single-arm study enrolled 29 patients aged 18–80 years with histologically confirmed, newly diagnosed PCNSL and measurable CNS lesions.
- Patients received intravenous rituximab (375 mg/m² on day 0), HD-MTX (3.5 g/m² on day 1) or temozolomide (TMZ; 150 mg/m², days 1–5 for MTX-intolerant patients), and continuous oral zanubrutinib (160 mg twice daily) in 28-day cycles.
- ORR was 89.7 %, with a CR rate of 89.7%. At a median follow-up of 16.2 months, the estimated 2-year PFS and OS were 82.8% and 95.2%, respectively.
- Treatment was generally well tolerated. The most common Grade ≥3 AEs included leukopenia (17.2%), neutropenia (17.2%), and thrombocytopenia (17.2%).
- These findings support combination of zanubrutinib, rituximab, and HD-MTX as first-line therapy for newly diagnosed PCNSL demonstrates promising efficacy and manageable toxicity warranting further investigations.
Reference
Xia Z et al. Zanubrutinib, Rituximab, and High-dose Methotrexate as First-line Treatment in Newly Diagnosed Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (Zana): A Prospective, Single-arm Study. 67th Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2025, abs25-418.